De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a painful condition affecting the tendons on the thumb side of your wrist. It occurs when the two tendons around the base of the thumb become inflamed, leading to pain and swelling near the thumb and lower arm. This inflammation can cause discomfort when forming a fist, grasping objects, or turning the wrist.
Understanding De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
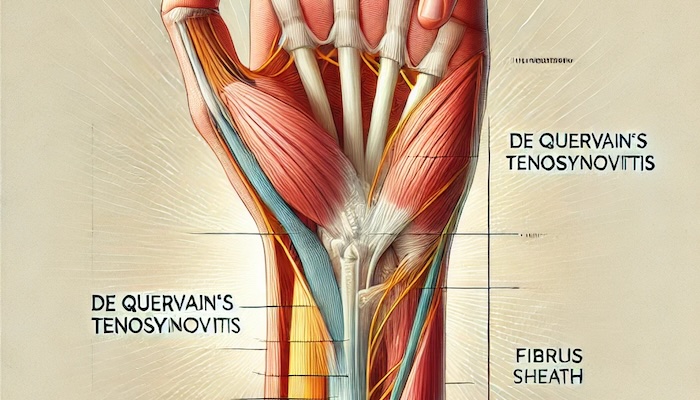
The condition primarily involves the abductor pollicis longus (APL) and extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) tendons. These tendons are responsible for moving the thumb away from the hand and extending it. They pass through a fibrous tunnel, or sheath, near the wrist. When these tendons become irritated or constricted, it leads to the characteristic pain and swelling of De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis:
- Repetitive Hand or Wrist Movements: Activities that involve repetitive thumb motions, such as typing, texting, or playing certain sports, can strain the tendons.
- Direct Injury: A direct blow to the thumb or wrist can cause scar tissue formation, restricting tendon movement.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis can increase the risk of tendon inflammation.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to fluid retention and swelling, affecting the tendons.
Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- Pain Near the Base of the Thumb: This pain may develop gradually or suddenly and is often felt when using the thumb and wrist.
- Swelling Near the Thumb: Swelling may be accompanied by a fluid-filled cyst in some cases.
- Difficulty Moving the Thumb and Wrist: Activities requiring a firm grip or pinching may be particularly painful.
- A "Sticking" or "Stop-and-Go" Sensation: You might feel a catching or snapping sensation when moving the thumb.
Diagnosis
A healthcare provider typically diagnoses De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis through a physical examination. One common test is the Finkelstein test, where you bend your thumb across the palm and bend your fingers down over the thumb, then bend your wrist toward the little finger. If this movement causes pain on the thumb side of the wrist, it may indicate De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis.
Interventional Pain Management Approaches
Interventional pain management offers several techniques to alleviate the symptoms of De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injecting corticosteroids into the tendon sheath can reduce inflammation and pain.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP involves injecting a concentration of the patient’s own platelets to promote healing in the affected tendons.
- Stem Cell Therapy: This regenerative treatment uses stem cells to repair damaged tissues and reduce inflammation.
- Acupuncture: Inserting thin needles at specific points may help alleviate pain and promote healing.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
In addition to interventional procedures, other non-surgical treatments include:
- Splinting: Immobilizing the thumb and wrist can help rest the tendons and reduce inflammation.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen the thumb and wrist muscles can improve function and decrease symptoms.
Surgical Intervention
If symptoms persist despite conservative treatments, surgical intervention may be considered. The procedure involves releasing the sheath around the tendons to allow them to glide more freely. Recovery includes physical therapy to restore strength and range of motion.
Preventive Measures
To prevent De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis, consider the following:
- Avoid Repetitive Movements: Take breaks during activities that involve repetitive thumb or wrist motions.
- Use Proper Ergonomics: Ensure that workspaces and tools are designed to minimize strain on the hands and wrists.
- Strengthening Exercises: Regular exercises to strengthen the wrist and thumb muscles can provide support to the tendons.
Conclusion
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis is a manageable condition with various treatment options available. Early intervention, particularly through interventional pain management techniques, can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the need for surgical procedures. If you experience symptoms, consult a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan.
Precision Pain Care and Rehabilitation has two convenient locations in Richmond Hill – Queens, and New Hyde Park – Long Island. Call the Queens office at (718) 215-1888 or (516) 419-4480 for the Long Island office to arrange an appointment with our Interventional Pain Management Specialists, Dr. Jeffrey Chacko or Dr. Sonny Ahluwalia.