Olecranon bursitis, commonly known as "student's elbow," is an inflammation of the bursa located over the olecranon process at the elbow's tip. This condition can cause pain, swelling, and limited elbow movement, affecting daily activities and quality of life. Interventional pain management offers effective strategies to alleviate symptoms and address the underlying causes of olecranon bursitis.
Understanding Olecranon Bursitis
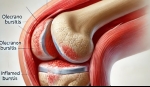
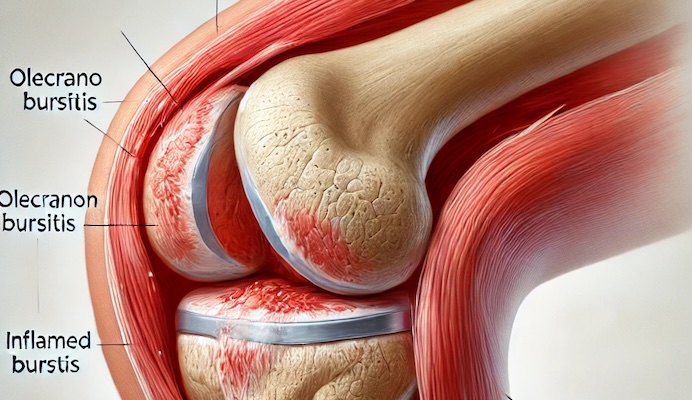
A bursa is a small, fluid-filled sac that reduces friction between bones and soft tissues. The olecranon bursa, situated between the skin and the olecranon (the pointed bone at the elbow's end), allows smooth movement of the skin over the bone. When this bursa becomes inflamed due to injury, prolonged pressure, infection, or underlying medical conditions like gout or rheumatoid arthritis, it leads to olecranon bursitis.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common symptoms include:
- Swelling: A noticeable lump at the elbow's tip.
- Pain: Ranging from mild to severe, especially when bending the elbow.
- Redness and Warmth: Indicating possible infection.
- Limited Mobility: Difficulty in fully extending or flexing the elbow.
Diagnosis involves a physical examination and may include imaging studies like X-rays or ultrasounds to assess the extent of inflammation and rule out other conditions. Aspiration of bursal fluid might be performed to check for infection or crystal deposits.
Interventional Pain Management Approaches
Interventional pain management focuses on minimally invasive techniques to relieve pain and improve function. For olecranon bursitis, treatment options include:
- Aspiration and Corticosteroid Injection: Removing excess fluid from the bursa can reduce pressure and pain. Injecting a corticosteroid afterward helps decrease inflammation. This procedure is typically performed under sterile conditions to minimize infection risk.
- Physical Therapy: A tailored exercise program can strengthen surrounding muscles, improve joint function, and prevent recurrence. Therapists may also use modalities like ultrasound or electrical stimulation to reduce pain and swelling.
- Activity Modification: Identifying and altering activities that exacerbate symptoms is crucial. Using protective elbow pads can cushion the area and prevent further irritation.
- Medication Management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be prescribed to manage pain and reduce inflammation. In cases of infection, appropriate antibiotics are necessary.
- Surgical Intervention: Reserved for chronic cases unresponsive to conservative treatments, surgical removal of the bursa (bursectomy) may be considered. This procedure is typically followed by rehabilitation to restore function.
Case Study Example
Consider a patient presenting with a swollen, painful elbow after prolonged desk work. Physical examination reveals tenderness over the olecranon, and ultrasound confirms bursitis without infection. The patient undergoes aspiration and receives a corticosteroid injection, followed by a structured physical therapy program focusing on ergonomic adjustments and strengthening exercises. Within weeks, the patient reports significant pain reduction and returns to normal activities without recurrence.
Data and Outcomes
Studies indicate that aspiration combined with corticosteroid injection provides significant symptom relief in non-infectious olecranon bursitis. A review in The Journal of Hand Surgery notes that this approach effectively reduces inflammation and accelerates recovery.
Additionally, incorporating physical therapy enhances functional outcomes and reduces the likelihood of recurrence.
Preventive Measures
To prevent olecranon bursitis:
- Avoid Prolonged Pressure: Use cushioning when resting elbows on hard surfaces.
- Protective Gear: Wear elbow pads during activities that risk elbow injury.
- Prompt Treatment: Address minor injuries or infections near the elbow promptly to prevent bursal inflammation.
Conclusion
Olecranon bursitis, while often manageable, can significantly impact daily life if not properly treated. Interventional pain management offers effective, minimally invasive solutions to alleviate symptoms and address underlying causes. Early intervention, combined with preventive strategies, ensures optimal recovery and reduces the risk of recurrence.
For personalized evaluation and treatment options, consulting with a specialist in interventional pain management is recommended.
Precision Pain Care and Rehabilitation has two convenient locations in Richmond Hill – Queens, and New Hyde Park – Long Island. Call the Queens office at (718) 215-1888 or (516) 419-4480 for the Long Island office to arrange an appointment with our Interventional Pain Management Specialists, Dr. Jeffrey Chacko or Dr. Sonny Ahluwalia.