Hip arthritis is a common yet often misunderstood condition that can significantly affect quality of life. Characterized by the deterioration of the cartilage in the hip joint, it leads to pain, stiffness, and difficulty in performing everyday activities. With advancements in medicine, particularly interventional pain management, there are effective ways to manage this condition and regain mobility and independence.
What is Hip Arthritis?
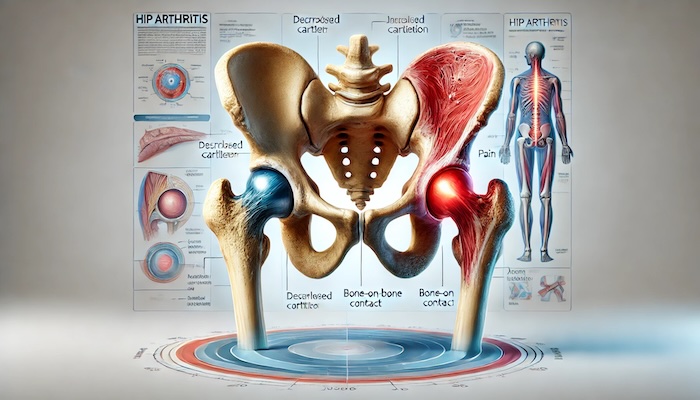
Arthritis in the hip commonly refers to osteoarthritis (OA), although rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and post-traumatic arthritis can also affect the hip joint. Let’s break these down:
- Osteoarthritis (OA): This is the "wear and tear" form of arthritis. Over time, the cartilage that cushions the hip joint wears away, leading to bone-on-bone contact. This causes pain, swelling, and limited range of motion.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks the lining of the joints, including the hip. This results in inflammation and can lead to joint destruction if untreated.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Occurs after an injury to the hip, such as a fracture or dislocation. Trauma can accelerate cartilage breakdown, leading to arthritis.
Regardless of the type, the symptoms of hip arthritis typically include:
- Pain in the groin, buttocks, or thigh.
- Stiffness that makes walking, bending, or standing up challenging.
- A grinding or popping sensation during movement.
- Weakness or a feeling of instability in the hip joint.
Risk Factors for Hip Arthritis
While aging is the primary risk factor, other contributors include:
- Genetics: Family history of arthritis can increase susceptibility.
- Obesity: Excess weight places additional stress on the hip joint.
- Joint Injuries: Sports injuries or accidents can damage the joint and increase arthritis risk.
- Repetitive Strain: Jobs or activities that involve repetitive hip movements can accelerate wear and tear.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Conditions like RA predispose the hip joint to damage.
How is Hip Arthritis Diagnosed?
A proper diagnosis involves a combination of:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will assess symptoms, movement limitations, and areas of pain.
- Imaging Studies:
- X-rays can reveal cartilage loss, bone spurs, or joint space narrowing.
- MRI may be used to detect early cartilage damage or inflammation.
- Lab Tests: Blood tests can help diagnose inflammatory types of arthritis, like RA.
Interventional Pain Management for Hip Arthritis
Interventional pain management focuses on minimally invasive treatments that address pain at its source while delaying or avoiding surgery. Here’s how these techniques help manage hip arthritis effectively:
1. Corticosteroid Injections
- Corticosteroids are injected directly into the hip joint to reduce inflammation.
- Offers temporary relief lasting weeks to months, especially for acute flare-ups.
2. Viscosupplementation
- Involves injecting hyaluronic acid into the joint to improve lubrication and reduce pain.
- Most effective in early stages of arthritis.
3. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
- PRP uses a concentration of platelets from your own blood to promote healing and reduce inflammation in the hip joint.
- This regenerative treatment is growing in popularity due to its natural approach and long-lasting effects.
4. Nerve Blocks
- Anesthetic is injected around specific nerves to block pain signals.
- Provides temporary relief and allows patients to engage in physical therapy.
5. Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA)
- Uses heat generated by radio waves to target and deactivate nerves that transmit pain from the hip joint.
- Offers long-lasting relief, especially for chronic pain.
6. Stem Cell Therapy
- A cutting-edge treatment that uses stem cells to regenerate damaged cartilage and reduce inflammation.
- Still under research but has shown promise in slowing arthritis progression.
Complementary Treatments
Along with interventional techniques, a combination of lifestyle changes and complementary therapies can significantly improve outcomes:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises improve joint stability, strengthen surrounding muscles, and enhance flexibility. Low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling are especially beneficial.
- Acupuncture: This ancient practice stimulates nerves, muscles, and connective tissue to alleviate pain and promote healing.
- Assistive Devices: Using canes or walkers can reduce stress on the hip and prevent further joint damage.
- Weight Management: Shedding even a small amount of weight can relieve pressure on the hip joint, improving symptoms significantly.
- Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids (e.g., salmon, walnuts) and antioxidants (e.g., berries, spinach) can help reduce inflammation in the body.
When is Surgery Necessary?
While most patients can manage hip arthritis with interventional treatments and lifestyle modifications, surgery may be necessary for severe cases where conservative measures fail. Surgical options include:
- Hip Resurfacing: An alternative to total hip replacement, this procedure reshapes the damaged bone and caps it with metal.
- Total Hip Replacement (Arthroplasty): Replaces the damaged joint with a prosthetic one. This is often a last resort but provides excellent pain relief and improved mobility.
Preventing Hip Arthritis Progression
While hip arthritis cannot always be prevented, certain strategies can slow its progression:
- Stay Active: Regular exercise keeps joints flexible and strengthens the muscles supporting the hip.
- Protect Your Joints: Avoid high-impact activities or repetitive movements that strain the hip.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reducing stress on your hip can significantly delay the onset of arthritis.
- Seek Early Treatment: Don’t ignore hip pain or stiffness. Early intervention can prevent further damage.
Living Well with Hip Arthritis
Managing hip arthritis is about taking proactive steps to reduce pain and maintain mobility. With advancements in interventional pain management, patients now have access to effective, minimally invasive treatments tailored to their needs.
At Precision Pain Care and Rehabilitation, we specialize in comprehensive care that empowers patients to live healthier, more active lives despite arthritis. Whether you’re seeking non-surgical options or guidance on managing symptoms, we’re here to help.
Precision Pain Care and Rehabilitation has two convenient locations in Richmond Hill – Queens, and New Hyde Park – Long Island. Call the Queens office at (718) 215-1888 or (516) 419-4480 for the Long Island office to arrange an appointment with our Interventional Pain Management Specialists, Dr. Jeffrey Chacko or Dr. Sonny Ahluwalia.
Note: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.