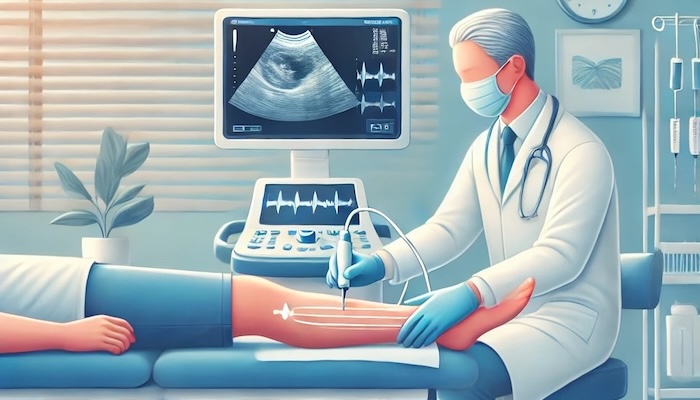
Tendonitis is a common condition that can cause significant discomfort and disrupt daily activities. It occurs when a tendon—the thick, fibrous cord connecting muscle to bone—becomes inflamed due to overuse, injury, or age-related degeneration. At Precision Pain Care and Rehabilitation, our focus on interventional pain management provides advanced treatment options to help patients find relief and regain mobility. This blog explores tendonitis, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and how interventional pain management can be an effective approach for long-term recovery.
What is Tendonitis?
Tendonitis, also referred to as tendinitis, is the inflammation or irritation of a tendon. This condition is often associated with repetitive motions, prolonged overuse, or sudden injuries. Common areas affected by tendonitis include the shoulders, elbows, wrists, knees, and heels. Recognizable conditions like "tennis elbow," "golfer’s elbow," "jumper’s knee," and "Achilles tendonitis" are specific forms of tendonitis.
What Causes Tendonitis?
Tendonitis typically results from repetitive stress or overuse of a particular tendon. Athletes, manual laborers, and individuals who perform repetitive tasks (e.g., typing, gardening, or lifting) are at higher risk of developing tendonitis. Other causes include:
- Age: Tendons lose elasticity and strength, increasing the risk of inflammation.
- Injuries: Sudden trauma, such as falling or twisting, can inflame the tendon.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or diabetes can contribute to tendon irritation.
- Improper Technique: Poor posture or incorrect technique during physical activities can strain tendons, leading to inflammation.
Symptoms of Tendonitis
Tendonitis symptoms can vary depending on the affected area, but common indicators include:
- Pain: A dull ache that worsens with movement.
- Tenderness: Sensitivity to touch around the tendon.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the joint or tendon.
- Stiffness: Difficulty moving the affected area, especially after periods of rest.
Diagnosing Tendonitis
A proper diagnosis begins with a thorough physical examination and a detailed medical history. Physicians may also recommend imaging tests such as:
- X-rays: To rule out fractures or other bone-related conditions.
- Ultrasound or MRI: To assess tendon inflammation, tears, or structural abnormalities.
Conventional Treatments for Tendonitis
Managing tendonitis often starts with conservative treatments, including:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities exacerbating the pain allows the tendon to heal.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to reduce inflammation and numb the pain.
- Medication: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can provide temporary relief.
- Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises to strengthen the affected area and improve flexibility.
- Bracing or Splinting: Using supportive devices to immobilize the tendon and promote healing.
While these methods can be effective, some cases of tendonitis persist or worsen, requiring more advanced interventions.
The Role of Interventional Pain Management in Treating Tendonitis
At Precision Pain Care and Rehabilitation, interventional pain management provides cutting-edge techniques to address tendonitis when traditional treatments fall short. Here are some innovative options:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Corticosteroids are anti-inflammatory medications injected directly into the inflamed tendon or surrounding area to reduce pain and swelling. These injections can provide immediate relief but are typically reserved for severe cases.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves using a patient’s blood, which is processed to concentrate platelets. Platelets release growth factors that promote tissue healing and repair. PRP injections have shown promising results in managing chronic tendonitis, especially for conditions like tennis elbow and Achilles tendonitis.
- Ultrasound-Guided Needle Tenotomy: This minimally invasive procedure uses ultrasound imaging to guide a fine needle into the affected tendon. The needle is used to break up scar tissue and stimulate the body’s natural healing response.
- Shockwave Therapy: Extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) uses high-energy sound waves to stimulate tendon healing and reduce pain. This non-invasive treatment is particularly effective for chronic tendonitis.
- Regenerative Medicine: Emerging therapies like stem cell injections are being explored for their potential to regenerate damaged tendon tissue and provide long-term relief.
- Nerve Blocks: In cases of severe pain, nerve blocks can temporarily interrupt pain signals, providing relief and facilitating physical therapy or other treatments.
Prevention Tips for Tendonitis
Preventing tendonitis is crucial, particularly for individuals at higher risk. Simple lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing this condition:
- Warm-Up and Stretch: Always warm up before physical activity and stretch afterward to maintain flexibility.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Ensure your workstation, tools, or sports equipment are ergonomically designed to reduce strain.
- Gradual Progression: Avoid overloading your body by gradually increasing the intensity and duration of physical activities.
- Cross-Training: Incorporate a variety of exercises to prevent repetitive strain on a single tendon.
- Listen to Your Body: Rest at the first signs of pain or discomfort to prevent further injury.
Real-Life Example: Managing Chronic Tendonitis
A patient, a 40-year-old avid tennis player, presented with chronic pain in their elbow that limited their ability to play and perform daily tasks. Despite months of rest, NSAIDs, and physical therapy, the pain persisted. At Precision Pain Care and Rehabilitation, an ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection provided immediate relief, followed by PRP therapy to promote long-term healing. Within weeks, the patient reported improved mobility and a return to regular activities.
The Data Behind Interventional Pain Management
Studies show that advanced treatments like PRP therapy and ultrasound-guided interventions significantly improve outcomes for tendonitis patients. For example:
- PRP Therapy: A 2023 study found that PRP injections resulted in a 70% reduction in pain and improved functionality for patients with chronic elbow tendonitis.
- Shockwave Therapy: Research indicates that 80% of patients with Achilles tendonitis experienced significant improvement after shockwave therapy sessions.
These data underscore the effectiveness of interventional techniques in managing and treating tendonitis.
Take Control of Tendonitis
Tendonitis can be a frustrating and painful condition, but with the right care, recovery is possible. At Precision Pain Care and Rehabilitation, interventional pain management offers hope for patients seeking advanced, minimally invasive solutions. Whether you’re an athlete, a professional, or someone dealing with age-related tendon issues, we’re here to help you regain mobility and live pain-free.
Precision Pain Care and Rehabilitation has two convenient locations in Richmond Hill – Queens, and New Hyde Park – Long Island. Call the Queens office at (718) 215-1888 or (516) 419-4480 for the Long Island office to arrange an appointment with our Interventional Pain Management Specialists, Dr. Jeffrey Chacko or Dr. Sonny Ahluwalia.