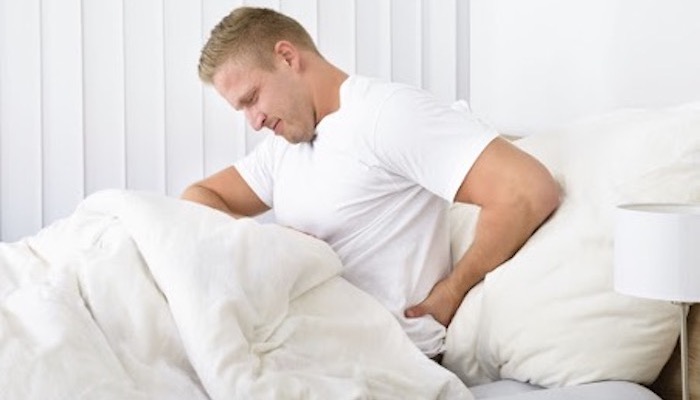
If you have lower back pain or sciatica, you probably want to know how to relieve your pain and prevent flareups or recurrences. Avoiding bed rest and staying active can help you do both.
Staying active can include a combination of strategies, such as continuing your daily activities, adding a simple exercise, such as short walks, and/or following a structured and guided exercise program.
This blog explains the potential side effects of continued bed rest and the unique benefits of engaging in low-impact physical activities with back pain.
How Prolonged Bed Rest May Worsen Your Back Pain
While you may want to lie down for a while if your back pain is severe, prolonged bed rest may not be a good option to treat your aching back. When you lie down for extended hours and minimize physical activity, the following changes may take place in your spine:
Deconditioning of Muscles
The extensor and flexor muscles of your spine that aid in forward and backward bending movements become weak and reduce in mass (atrophy). These muscles, especially the erector spinae and multifidus are important stabilizers of your back and help withstand compressive loads.
Changes In Disc Size
When you lie down, the size of your intervertebral disc increases due to swelling by the absorption of fluids. The risk of injury, such as herniation is high during this period, especially during bending movements.
Alteration In Spinal Biomechanics
Prolonged periods of lying down alter the normal lordotic (reverse-C shape) curve of your lower spine and makes it flatter, altering the normal mechanics of your spine.
Higher Risk of Injury
The above changes can make your back weak and worsen your pain. Additionally, these changes pose a higher risk of injury due to spinal instability and insufficient load-bearing capacity of the spine.
2 Tips for Staying Active When You Have Back Pain
Engaging in physical activities can help enhance blood flow to the tissues in your back, improve muscle strength and flexibility, nourish your spinal discs, and make your joints and bones stronger.
Here are 2 tips to help you get started:
1. Combat the Immediate Pain
If your pain is preventing you from being active, use these effective measures, which may provide immediate pain relief:
- Ice therapy
- Heat therapy
- Topical analgesics
- Massage
Once your pain level has reduced, you will be able to engage in more physical movements.
2. Engage in Low-Impact Activities That Help Build Strength
Staying active when you have back pain doesn’t necessarily include performing high-impact pursuits. Start with low-impact activities, which can gradually build your strength and spinal stability with less exertion and fatigue, such as:
- Easy hamstring stretches
- Simple lower back exercises
- Beginner yoga poses for back pain
- Water (aquatic) therapy
It’s advisable to talk with your doctor or physical therapist before starting a new exercise program, especially if you’re having an acute back pain episode. If you experience sharp or sudden pain while exercising, stop right away and consult your doctor. Be sure to use correct posture, form, and technique when you perform the suggested activities.
Following these tips may help in long-term relief and lesser recurrences of back pain compared to bed rest. Staying consistent with any of the suggested low-impact activities can make a difference in your overall wellbeing and may significantly enhance your spinal health.
Precision Pain Care and Rehabilitation has two convenient locations in Richmond Hill – Queens and New Hyde Park – Long Island. Call the Richmond Hill office at (718) 215-1888, or (516) 419-4480 for the Long Island office, to arrange an appointment with our Interventional Pain Management Specialist, Dr. Jeffrey Chacko.